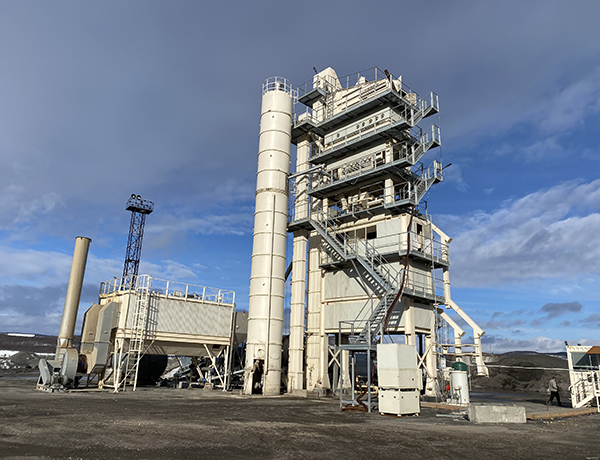
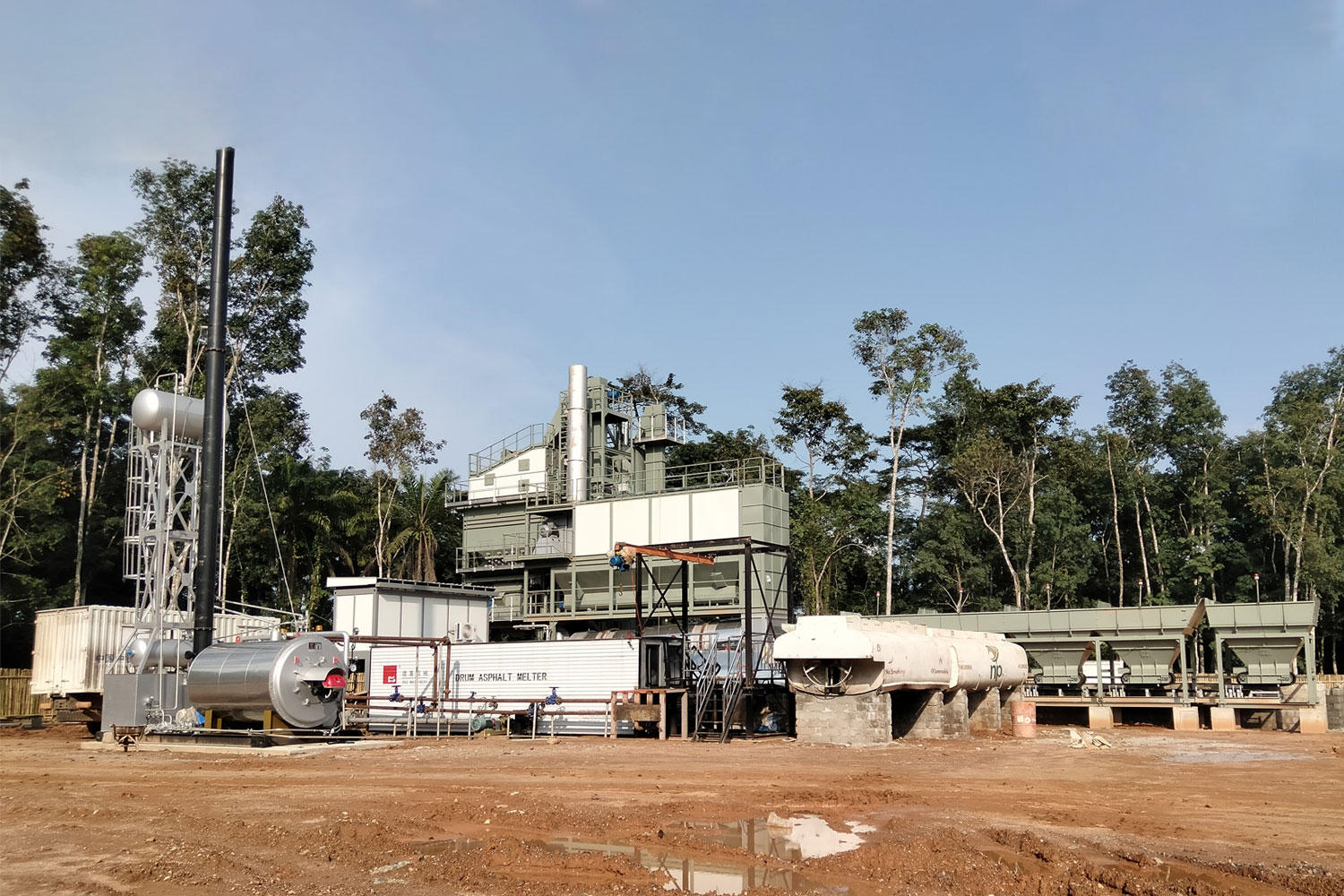
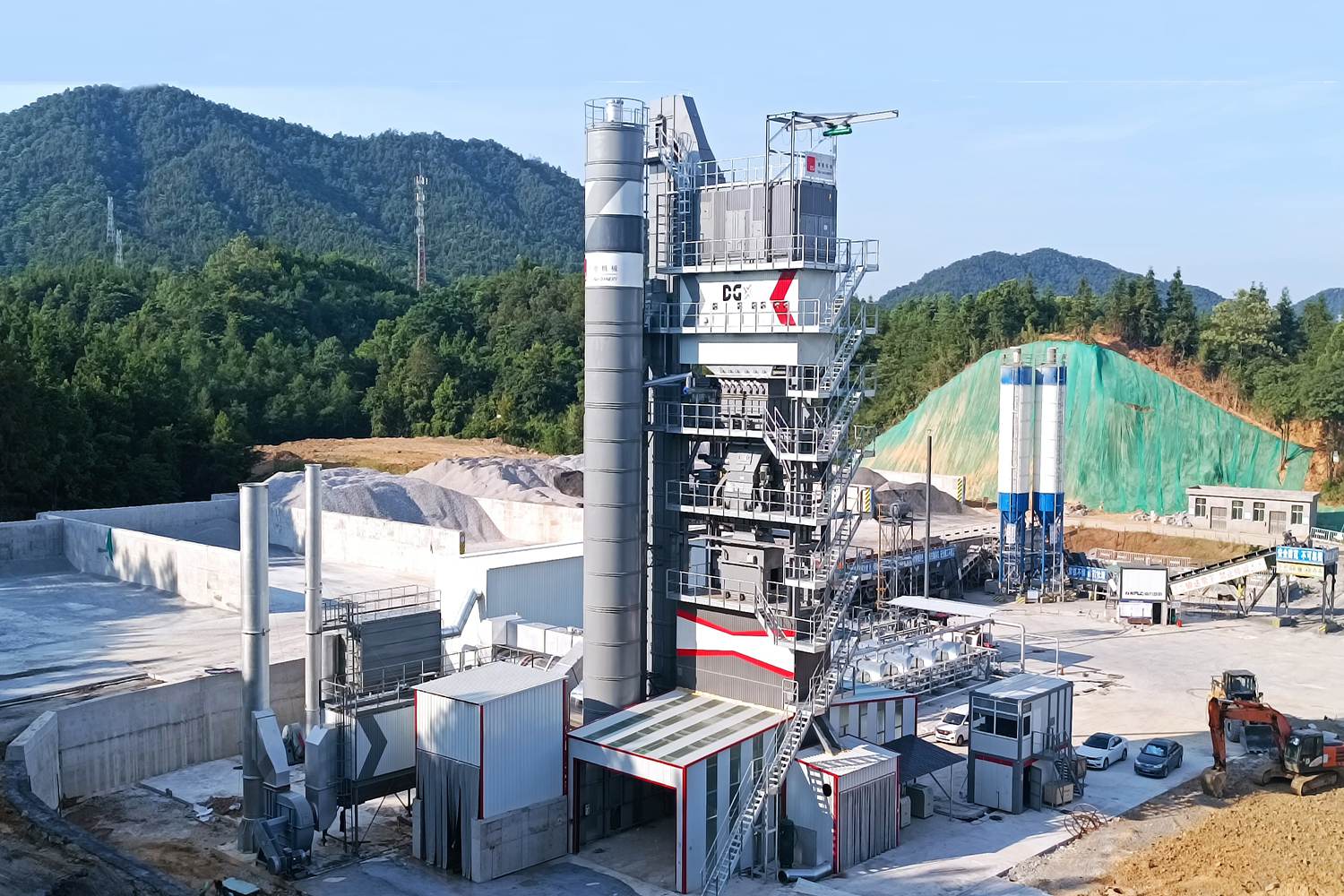
Hot Mix Batching Plants are essential facilities in the construction industry, particularly for paving and road repair. These plants are designed to produce asphalt concrete by mixing aggregates, asphalt binder, and additives at high temperatures. The primary advantage of using a hot mix plant is the ability to achieve a high-quality product that ensures durability and performance of the pavement. The plant operates on a continuous basis, allowing for efficient production and reducing waiting times for delivery to construction sites. The hot mix batching process typically involves several stages, including drying of aggregates, heating of asphalt binder, and mixing both components at precise ratios to achieve the desired blend. This process not only enhances the binding properties of the asphalt but also improves the workability and longevity of the finished product. Moreover, modern hot mix batching plants are increasingly incorporating advanced technology, such as automated systems and environmental controls, to optimize performance and minimize emissions. This focus on sustainability is becoming increasingly important as the industry aims to reduce its carbon footprint. Furthermore, with the growing demand for infrastructure development worldwide, hot mix batching plants play a pivotal role in ensuring that high-quality asphalt is readily available for various construction projects. Overall, the significance of hot mix batching plants cannot be overstated, as they are critical in supplying the necessary materials for building resilient and sustainable roadways that meet the challenges of modern transportation needs.
Content Disclaimer
The content provided on this website is for informational purposes only. Some of the information, articles, images, and other materials available on this site may be sourced from third-party websites and public domain resources. While we make every effort to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information, we do not take responsibility for the content provided by external sources.