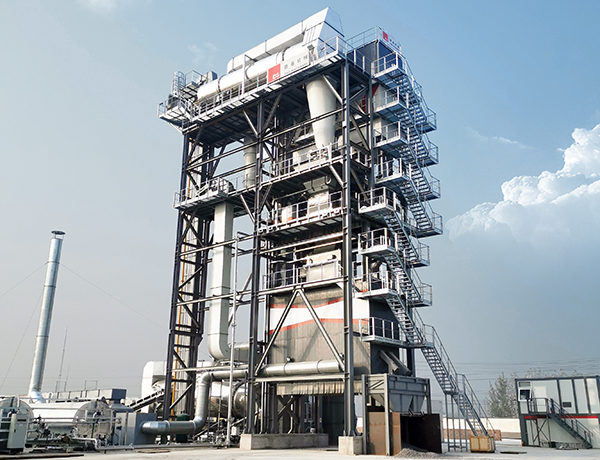
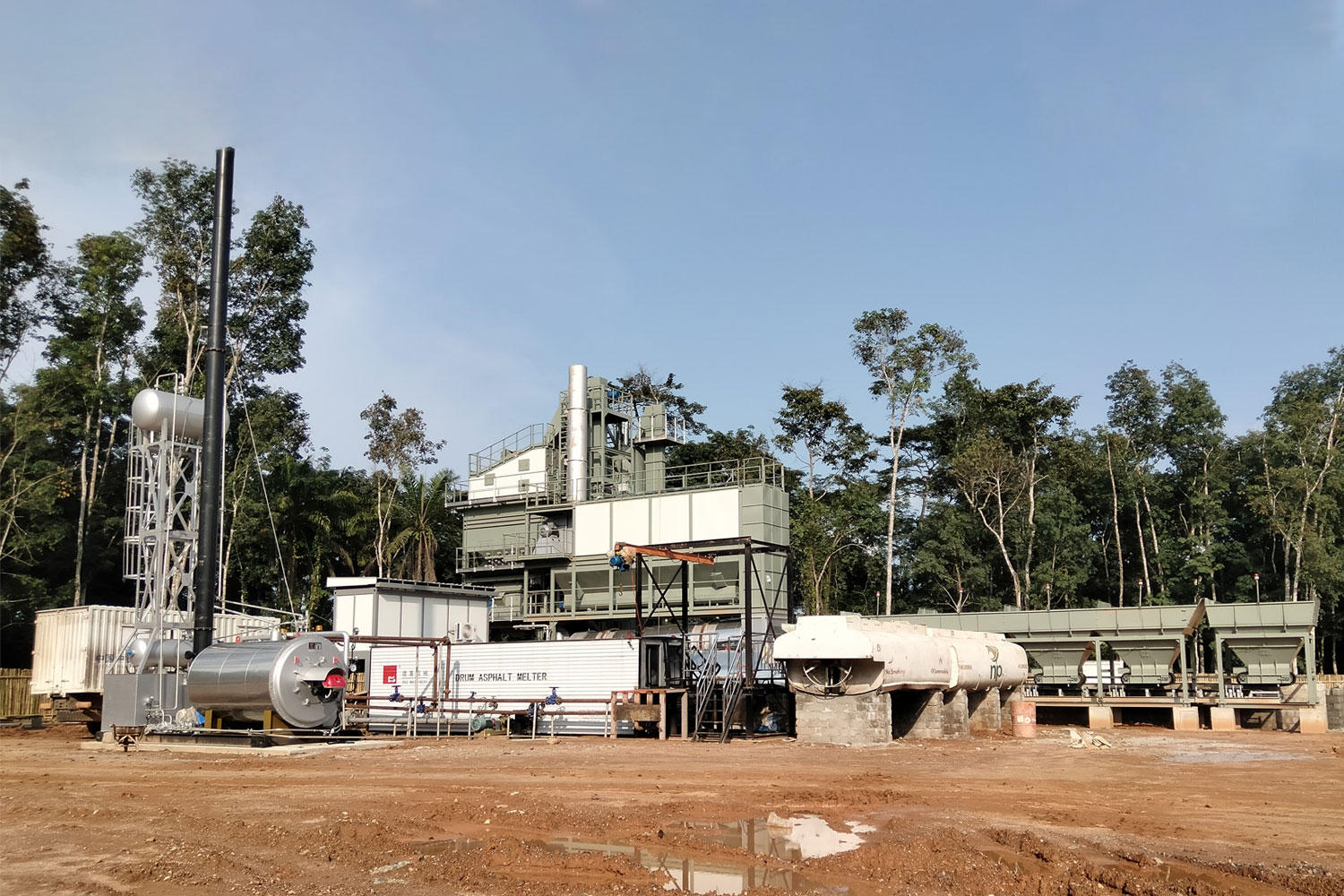
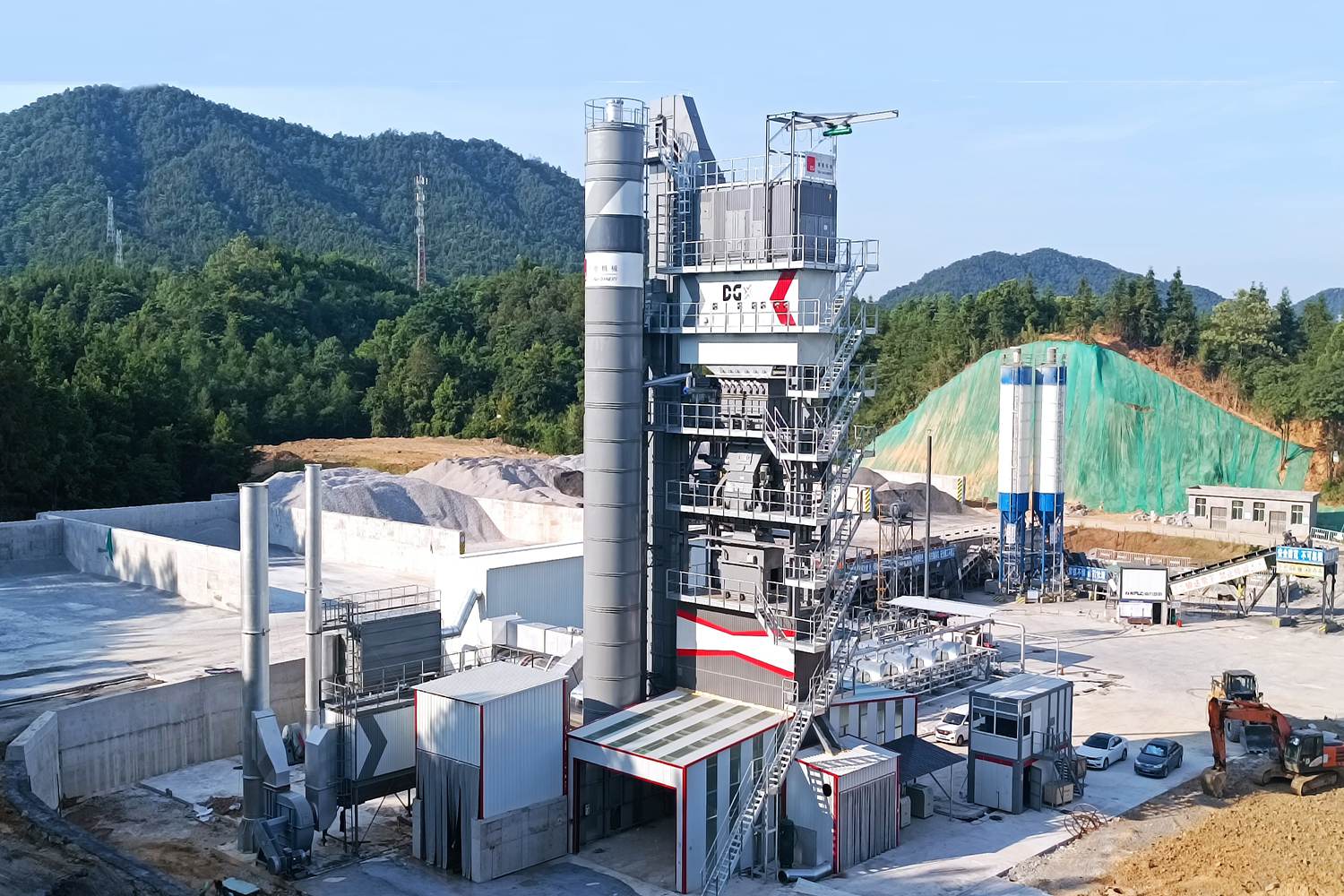
Asphalt production plants play a crucial role in the construction and maintenance of roadways, highways, and various infrastructure projects. These facilities are designed to produce asphalt concrete, a mixture of aggregates, liquid asphalt, and additives that provide the necessary durability and performance characteristics for paving applications. The process begins with the careful selection of raw materials, including gravel, sand, and crushed stone, ensuring that they meet required quality standards.
In the production phase, the aggregates are heated and thoroughly mixed with hot asphalt to achieve a homogenous blend. Advanced technologies are employed to control the temperature and consistency of the mix, paving the way for optimal performance in paving applications. Environmental considerations are also at the forefront, with many asphalt plants incorporating systems to reduce emissions and maximize energy efficiency.
Additionally, asphalt production plants can be categorized into various types, including batch and continuous mixing plants, each offering unique operational benefits and efficiencies. Batch plants are typically employed for smaller projects or where flexibility is essential, allowing for quick adjustments in production recipes. In contrast, continuous mixing plants are more suited for larger projects requiring high-volume outputs without sacrificing quality.
Furthermore, modern asphalt plants are increasingly incorporating recycling systems that enable the reuse of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). This not only supports sustainability efforts but also reduces material costs and environmental impact. As the demand for durable and sustainable road solutions grows, asphalt production plants will continue to evolve, integrating innovations in technology, materials, and production processes to meet the needs of the industry.
Content Disclaimer
The content provided on this website is for informational purposes only. Some of the information, articles, images, and other materials available on this site may be sourced from third-party websites and public domain resources. While we make every effort to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information, we do not take responsibility for the content provided by external sources.